Machine Learning
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Container manager: Currently tested on Docker and ContainerD.
- Access to a Kubernetes cluster.
kubectlinstalled and configured.
Deploy
To enable machine learning-based data prediction in OpenTwins, you must integrate Kafka-ML along with a service that supplies the required input data for the models. Refer to the architecture documentation to understand how this component interacts with the overall system.
Although OpenTwins includes two built-in services for this purpose, they both depend on Eclipse Hono, which we currently do not recommend. We strongly advise developing a custom service that sends input data to the Kafka-ML topic, ensuring it aligns with the specific requirements of your digital twin. This service can obtain the data from the related digital twin as well as from other twins, either real-time via Eclipse Ditto or historical from InfluxDB.
Kafka-ML
To install Kafka-ML, follow the official instructions in its GitHub repository. Kafka-ML can be deployed in a Kubernetes cluster (recommended) or locally, depending on your infrastructure needs.
Kafka-ML facilitates seamless integration of machine learning models with Kafka. It provides the capability to:
- Upload models from TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Train models directly within the system.
- Deploy models for real-time inference using Kafka streams.
The Kafka-ML workflow is as follows:
- Input data is sent through a designated Kafka topic to trigger model inference.
- Kafka-ML processes the data and runs the prediction.
- The predicted results are returned via an output Kafka topic.
For an in-depth understanding of Kafka-ML’s features and configuration, we highly recommend consulting the official user guide available in its GitHub repository.
In OpenTwins documentation, we assume that models are already deployed, trained, and ready for inference within Kafka-ML.
Eclipse Hono to Kafka-ML
This component is currently unused because Eclipse Hono has been deprecated.
The plan is to migrate this component to the new architecture so that it reads data directly from Eclipse Ditto, ensuring a more efficient and scalable integration.
Error detection for Eclipse Hono with Kafka-ML
This component is currently unused because Eclipse Hono has been deprecated.
The plan is to migrate this component to the new architecture so that it reads data directly from Eclipse Ditto, ensuring a more efficient and scalable integration.
Connect
To integrate Kafka-ML with OpenTwins, you need to establish an Eclipse Ditto connection in OpenTwins. This connection enables OpenTwins to receive data from Kafka-ML and update the corresponding digital twin. The process involves defining an Eclipse Ditto JavaScript mapping to convert incoming messages into the Ditto Protocol.
The connection must follow this data flow:
- Kafka-ML generates predictions and send data to Apache Kafka.
- Eclipse Ditto receives the data via a configured connection.
- The JavaScript mapping in Eclipse Ditto processes the data and updates the corresponding digital twin in OpenTwins.
Connection example
Consider a machine learning model in Kafka-ML that predicts humidity and temperature for a device. The model outputs data in the format [humidity, temperature].
In OpenTwins, a twin exists with the ID example:sensor, containing two features: humidity and temperature. Each feature in Eclipse Ditto must include properties and a value. The following image shows the structure of the digital twin in Eclipse Ditto:

To establish the connection between Kafka-ML and OpenTwins, you need to create an Apache Kafka connection in Eclipse Ditto. This connection receives and transforms predictions from Kafka-ML.
In the connection, a JavaScript mapping must be defined to transform messages from Apache Kafka. The mapping reads incoming messages, converts them to JSON, extracts values for each feature, and formats the message according to the Ditto Protocol before sending it. The function name mapToDittoProtocolMsg and the return Ditto.buildDittoProtocolMsg must always be included. The return value can be a single Ditto message or a list of Ditto messages.
Here is the JavaScript mapping for this example:
function mapToDittoProtocolMsg(headers, textPayload, bytePayload, contentType) {
const jsonData = JSON.parse(textPayload);
const humidity = jsonData[0];
const temperature = jsonData[1];
headers = Object.assign(headers, { 'Content-Type': 'application/merge-patch+json' });
var features = {
humidity: {
properties: {
value: humidity
}
},
temperature: {
properties: {
value: temperature
}
}
};
return Ditto.buildDittoProtocolMsg(
'example',
'sensor',
'things',
'twin',
'commands',
'merge',
'/features',
headers,
features
);
}
In OpenTwins, there are two ways to create the connection: via the OpenTwins UI or the Eclipse Ditto API. In both cases we recommend to refer to the Eclipse Ditto documentation.
- OpenTwins UI
- Eclipse Ditto API
In Grafana, open the OpenTwins app from the left-side menu.
Navigate to the Connections section and click Create new connection.
Select Kafka as the connection type and fill in the required details for the Apache Kafka broker.
- Provide a unique identifier for the connection (avoid special characters except -).
- If authentication is required, include the username and password in the URI.
- The bootstrap servers usually match the URI.
- Leave other fields as default unless necessary.
Under Message Mapping, click Add JavaScript Mapping, enter an identifier, and paste the JavaScript code from above.
Under Sources, click Add Source, then:
- Specify the Kafka topic where Kafka-ML outputs predictions.
- Set Authorization Context to
pre-authenticated:kafkaml-connection. - Select the previously defined JavaScript mapping under Payload Mapping.
Click Create Connection. If a success message appears, the Kafka-ML model is now connected.
If you are using Minikube, you must expose the Eclipse Ditto nginx service in order to access it from your localhost. To do this, find the name of the service with kubectl get services and then run minikube service <service-name> --url.
Open an API tool such as Postman.
Create a JSON payload for the connection configuration based on the Eclipse Ditto documentation.
Embed the JavaScript mapping within the JSON configuration.
- Ensure all lines end with semicolons (;).
- Use single quotes ('), not double quotes (").
- Remove all line breaks.
- If issues arise, replace single quotes with \u0027.
Add the source configuration, including the Kafka topic and JavaScript mapping identifier. Example JSON payload for output topic
kafkaml-output-topic:{
"name": "kafkaml-source-connection",
"connectionType": "kafka",
"connectionStatus": "open",
"uri": "tcp://{KAFKA-IP}:{KAFKA-PORT}",
"specificConfig": {
"saslMechanism": "plain",
"bootstrapServers": "{KAFKA-IP}:{KAFKA-PORT}"
},
"sources": [
{
"addresses": [
"kafkaml-output-topic"
],
"qos": 1,
"authorizationContext": [
"pre-authenticated:kafkaml-connection"
],
"payloadMapping": [
"jsmapping"
]
}
],
"targets": [],
"clientCount": 1,
"mappingDefinitions": {
"jsmapping": {
"mappingEngine": "JavaScript",
"options": {
"incomingScript": "function mapToDittoProtocolMsg(headers, textPayload, bytePayload, contentType) { const jsonData = JSON.parse(textPayload); const humidity = jsonData[0]; const temperature = jsonData[1]; headers = Object.assign(headers, { 'Content-Type': 'application/merge-patch+json' }); var features = { humidity: { properties: { value: humidity } }, temperature: { properties: { value: temperature } } }; return Ditto.buildDittoProtocolMsg( 'example', 'sensor', 'things', 'twin', 'commands', 'merge', '/features', headers, features ); }"
}
}
},
"tags": []
}Send a PUT request to:
http://{ECLIPSE_DITTO_URI}/api/2/connections/{ID_CONNECTION}- Include the JSON payload created earlier as the request body.
- Replace
{ECLIPSE_DITTO_URI}with the corresponding Eclipse Ditto IP and port. - Replace
{ID_CONNECTION}with the desired connection identifier (e.g.,kafkaml-source-connection). - Use Basic Authentication with the default username (
devops) and password (foobar), or use the configured credentials.
Once the integration is complete, Kafka-ML predictions will be processed and updated in OpenTwins. For example, if Kafka-ML outputs [23.45, 23.12], the update message to digital twin will appear as follows:
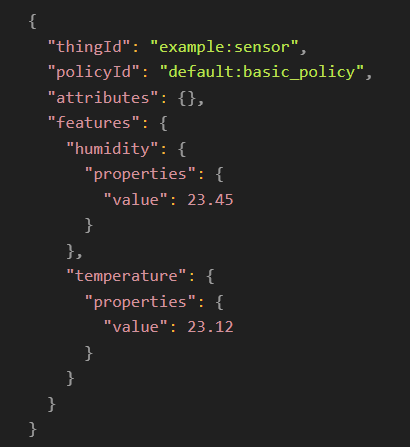
With this setup, a machine learning model in Kafka-ML and OpenTwins are connected. Once the model is activated (via a script or any other method you choose), the generated data will automatically update the specified digital twin according to your configured settings. Additionally, in InfluxDB, you can differentiate between generated and real data using the authorization context.